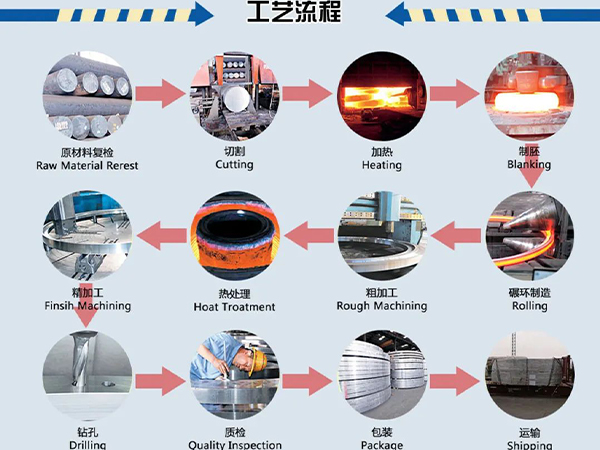
What is forging? What are the advantages of forging?
Forging is a metal processing technique that mainly applies external forces to cause plastic deformation of metal materials during the deformation process, thereby changing their shape, size, and microstructure.
The purpose of forging can be to simply change the shape of the metal, or to improve the strength, hardness, or other mechanical properties of the material.
Advantages of forging:
1. Improve mechanical performance: Forging can significantly enhance the strength, hardness, toughness, and wear resistance of metal materials. These performance improvements are mainly due to the changes in microstructure and texture of the metal during deformation.
2. Reduce internal stress: The plastic deformation generated during the forging process can effectively release the internal stress of the material, avoiding or reducing the occurrence of cracks or deformation during subsequent use.
3. Reduce processing time: Compared with other metal processing techniques such as casting and rolling, forging usually requires fewer working hours and processing equipment, resulting in lower production costs.
4. Improve mold life: During the forging process, the deformation of the metal is uniform, and the wear on the mold is relatively small, which helps to extend the mold life.
5. Better design freedom: Due to the fact that forging can directly form complex shapes, greater design freedom can be obtained to meet specific functional requirements.